Substrate. What replaces the soil. Technologies of cultivation.

What is necessary for plants? Of course the sun, air, and water. In addition, another major component: NUTRITION.
Plants receive basic nutrition through the root system in the form of dissolved chemicals in water, so that later, by photosynthesis, using light energy, convert carbon dioxide into building material to create its own cellular structure, that is, for its own growth, development, and fruiting.
For plants, various chemical elements are needed, the so-called "basic" elements - nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus, and a whole series of other chemical elements: magnesium, calcium, sulfur, and in very small quantities trace elements - manganese, iron, boron, zinc, copper, Molybdenum and others.
Where can plants get this set of chemicals? From the environment where the roots live, For example from the soil, or from a substrate. What is the substrate? It is a neutral substance into which the root system of plants is placed to effectively grow plants on hydroponics. A nutrient solution containing all the necessary chemical elements for the growth and development of plants is fed by means of an irrigation system into containers filled with a substrate, where it is absorbed by the root system of the plant and all the necessary nutrients enter the plant with irrigation water.
As substrates, mineral, or organic substances that are chemically neutral and stable, capable of remaining neutral when a solution of salts containing all that is necessary for the life of plants is fed to the plants. In addition, the substrate must have good water retention,
Industrial technologies for growing plants, when the farmer plans his harvest, are forcing more and more attention to effective hydroponic plant growing technologies and the choice of the optimal type of substrate.
Good fertile soils are not everywhere. Maintaining the soil in good condition, ensuring its fertility, also requires serious costs, and sometimes significant investments for its restoration, disinfection, and improvement of the structure. No matter how rich the soil is, over time its fertility is depleted and fertilization is required.
Traditional fertilization schemes are not very efficient, as crop plants receive only a fraction of the fertilizer applied to the soil. Partly fertilizers are used by weeds, partly they react with substances already contained in the soil, partly washed out by rains, partly they penetrate to great depths and get into underground groundwater, polluting them and salting the soil. Indoors, that is, in greenhouses, the intensive use of natural soil leads to its rapid depletion, salinization, a sharp decrease in fertility, the accumulation of pathogenic microflora, and pests in it. Because of this, greenhouse farms growing plants on the soil are forced to periodically replace the fertile soil layer with a new one, but this is associated with high labor costs and the problem of acquiring high-quality fertile soil for replacement.
Hydroponics, despite the fact that this technology requires strict adherence to all agrotechnical requirements and additional equipment for the preparation of nutrient solutions, accurate dosage of nutrients and automation of all processes related to irrigation and nutrition of plants, is gaining more and more recognition among people engaged in agriculture and cultivation. various plants.
STRAWBERRY FERTILIZER RECOMMENDATIONS
This section of this article is based on Haifa Chemicals materials for working with a hydroponic strawberry crop Growing on a substrate in a hydroponic greenhouse with hanging trays of strawberries
Planting density: 150,000 plants per hectare Expected yield: 90-100 tons per hectare.
| Growing season |
Weeks
|
N
|
P
|
K
|
Ca
|
Mg
|
|
--------------------- mg / l --------------------
|
| After landing |
1-6
|
110
|
33
|
140
|
106
|
50
|
| Young plants before flowering |
7-14
|
200
|
90
|
170
|
106
|
50
|
| Flowering - fruit ovary |
15-21
|
150
|
45
|
100
|
85-110
|
50
|
| Formation of berries |
22-25
|
120
|
20
|
100
|
85-110
|
30
|
| Harvest |
26-33
|
100
|
20
|
100
|
85-110
|
30
|
| Harvest |
34-35
|
100
|
20
|
100
|
85-110
|
30
|
| Harvest |
36-39
|
70
|
17
|
80
|
65-110
|
30
|
The calculation of the composition and concentration of nutrients is based on the results of the analysis of the parameters of the water used:
|
Irrigation water parameters (example).
|
|
Ca - 80 mg/l
Mg - 12 mg/l
HCO3 - 80 mg/l
EC - 0.5 ms/cm
|
|
pH
|
EC ms/cm
|
NH4/(NO3+NH4)
|
|
5.5-6.5
|
1.5-2.0
|
1/10
|
|
In case the pH of the water has a higher value, then it is reduced by adding acid to the irrigation water. The acid can be nitric acid or phosphoric acid. Phosphoric acid is preferable because it flushes the drip irrigation system and prevents calcium deposits from forming on the droppers, which prevents clogging.
In addition to macronutrients, the nutrient solution must also contain trace elements. As an option, trace elements can be applied through foliar feeding, that is, by spraying the leaf surface.
| Parameter |
The recommended concentration of trace elements
|
|
Growing on a substrate
|
|
Concentration of nutrients
|
| Trace elements(mg/l) |
| Fe |
1.117
|
| Mn |
0.549
|
| Zn |
0.458
|
| B |
0.270
|
| Cu |
0.048
|
| Mo |
0.048
|
All dosages of fertilizers, micro, and macronutrients are calculated based on the DV (active ingredient).
Recommendations for the preparation of the nutrient solution.
To prepare the nutrient solution, you must use a fertigation unit (solution unit). When growing strawberries using low-volume technology, it is recommended to use mortar units with a thin dosage of components and use at least 3 mother liquors to prepare the working solution. In the first container with the mother solution, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potash fertilizers are dissolved in appropriate proportions, in the second tank with mother liquor - calcium and magnesium fertilizers. The third tank is used for the acid mother liquor.
Mortar units can be of various designs, but the main requirement is an accurate dosage of mother liquors and a uniform, constant addition of fertilizers to irrigation water. It is imperative to control the total salt content in the EC working solution and its acidity pH.

Agrosheriff TST
We offer for this purpose the Agrosheriff TST climate controlled fertigation and automation system. The system is designed specifically for growing strawberries using low-volume technology, automatic control of irrigation and fertigation modes, as well as control of climatic parameters in the greenhouse, based on an industrial controller and a convenient computer program, allows you to optimize watering, plant nutrition and maintain optimal temperature and humidity parameters in the greenhouse ...
Open Field
Strawberries can be grown outdoors in a variety of ways. The most effective and productive way is growing berries on high ridges mulched with a special two-color mulching film, using drip irrigation for irrigation and a fertigation system for plant nutrition. The composition of the fertilizing solution in each case is determined independently, taking into account the presence of nutrients in the soil, based on the total plant nutrient requirements. The table above can be taken as a basis for plant needs in nutrients.
However, many growers still use traditional methods of fertilizing strawberry plantations, that is, applying dry granular fertilizers to the soil. In the traditional cultivation of strawberries in the open field and fertilizing the soil, the following fertilization rates are recommended in kilograms per hectare, in terms of on the active substance:
|
N
|
P2O5
|
K2O
|
CaO
|
MgO
|
|
150
|
150
|
240
|
120
|
60
|
The reader is solely responsible for any use of the information provided herein. Haifa Chemicals Ltd. and Agrosheriff Ltd. does not make any guarantees as to the absence of data errors. In addition, it does not guarantee the results that can be obtained from the use of this data, or the accuracy, reliability or content of any information provided.
Types of substrates
There are two types of substrates: mineral and organic. The first include mineral wool, expanded clay, crushed tuff, perlite, and vermiculite. The best of them are tuff, perlite, and vermiculite. They are chemically neutral and have good water retention properties. As for expanded clay and mineral wool, these substrates must be treated with a certain degree of caution, it is imperative to test and chemically analyze such substrates for the content of harmful chemicals, their chemical stability and the effect on acidity (Ph) and salt content (EC ), the effect on the change in the composition of the nutrient solution.
Recently quite popular substrates based on mineral wool, in addition to certain chemical instability, may also contain phenolic resins, which are added to them by some manufacturers to create and maintain the structure of the substrate. Phenolic resins decompose and release harmful chemicals into the environment.
Organic substrates have been known for a long time and are widely used in agriculture. In Russia, peat is traditionally most often used, and sometimes sawdust, bark, and straw are also used. Such substrates are used both independently and mixed with soil or compost, most often for growing seedlings and plants in greenhouses, and sometimes to improve soil properties.
 I believe that you are very familiar with the substrates mentioned above, so our story will be about a fairly new and, perhaps, the most productive and effective substrate made from the peel of coconuts. This is the Coconut substrate. Coconut substrate is becoming more and more popular due to its properties, which significantly exceed its characteristics all other known types of organic substrates.
I believe that you are very familiar with the substrates mentioned above, so our story will be about a fairly new and, perhaps, the most productive and effective substrate made from the peel of coconuts. This is the Coconut substrate. Coconut substrate is becoming more and more popular due to its properties, which significantly exceed its characteristics all other known types of organic substrates.
The main advantage of such a substrate is almost absolute chemical neutrality and inertness, light mechanical structure, high coefficient of water retention, excellent aeration, long service life. During its use, the substrate does not decompose and practically does not change its physicochemical properties. Coconut substrate can be used for growing plants in greenhouses for up to 3 years without replacement. Currently, many producers are switching to using this particular type of substrate, as the most optimal from the point of view of agricultural technology and cost-effective.
Coconut substrate
The basis of this substrate is coconut fiber, obtained from coconut shells. Our company started the co-production of a high-quality coconut substrate with our partners in Bangladesh about two years ago. You can order through our company, various types of coconut substrate produced using the most advanced technology. Only ripe nut peels are used as raw materials. The fiber undergoes double sieving, which allows removing from it all dust-like and small particles, which can lead to caking of the substrate and deterioration of aeration during the growing period. Raw materials (coconut shells) are specially aged for 14-18 months before the start of production of the substrate, so that in all biological processes of organic decomposition were completed there. This makes it possible to obtain a very stable, neutral substrate that does not subsequently change its properties and does not affect the composition and concentration of nutrients in the water solution supplied for irrigation.
Finished product
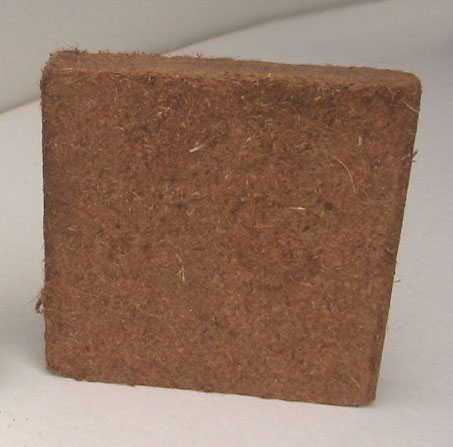
 No matter how good the substrate is, it still needs to be delivered to the farm. Carrying "air" at the current transport tariffs is very unprofitable.
No matter how good the substrate is, it still needs to be delivered to the farm. Carrying "air" at the current transport tariffs is very unprofitable.
To solve this problem, a technology for pressing the coconut substrate was developed, which made it possible to reduce its volume by 5-7 times! and it instantly straightens out, increasing in volume !!!
This is a very important point for the consumer. Transport costs are reduced several times. Well, of course, the space in the warehouse for storing the substrate is also needed several times less.
Products are produced in various versions, for example, pressed briquettes pressed substrate in special plastic bags that can be used for planting plants, special options for small packaging for summer residents, and gardeners. Special bags with a substrate for growing large-sized plants, ornamental plants and flowers are also produced Our latest development, special bags with coconut substrate, designed for growing strawberries using low-volume hydroponics technology.
Options:
There are various types of substrate packaging. Only a few of them are shown below.
 |
 |
| Products on Euro pallets, ready for shipment. |
5 kg. briquette in a dry and moist form. |
 |
 |
| Dry vegetable bag. |
Moistened vegetable bag. |
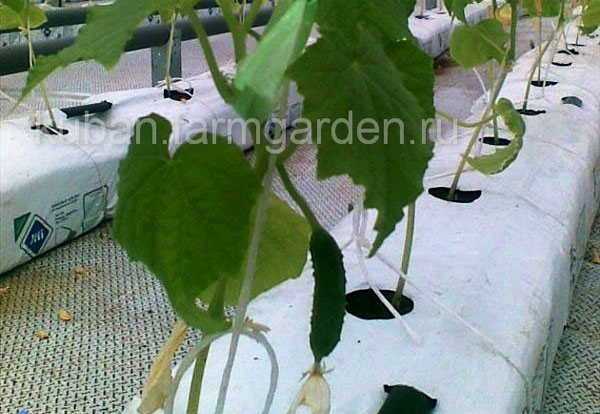

Growing cucumbers.
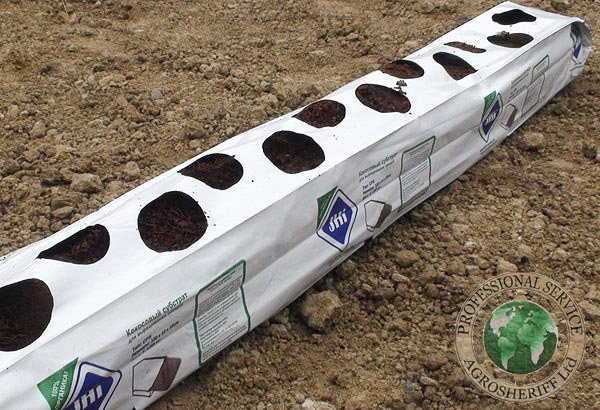

Package for low-volume hydroponics. Cultivation of strawberries.

Coconut tablet for flower growers.
Substrate application.
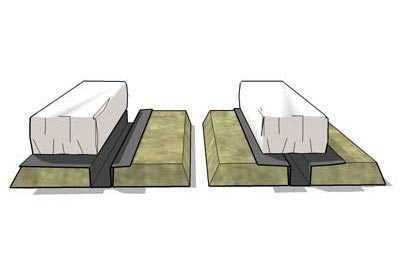
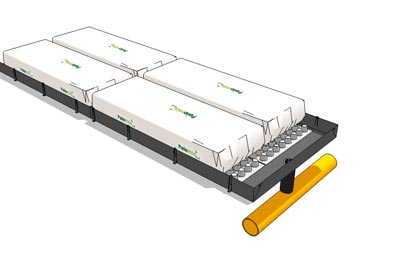
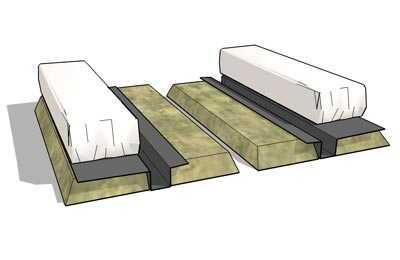
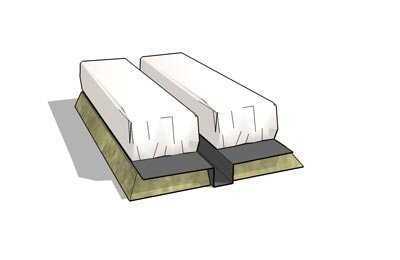
We offer you a number of photos without comment. Look at these photos, and we hope that everything will become clear to you.
 |
 |
 |
 |
| |
|
Containers for the substrate.
|
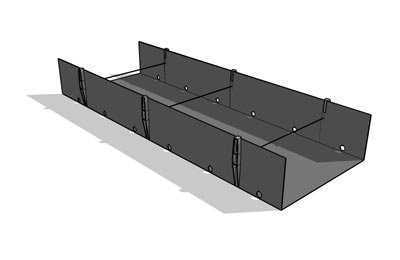 |
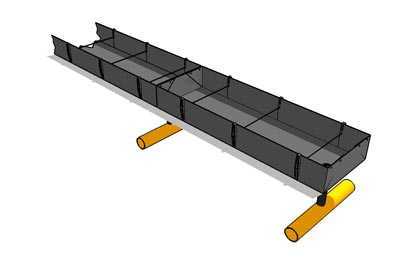 |
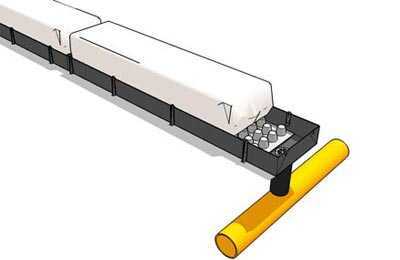 |
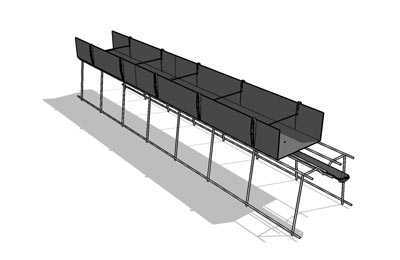 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
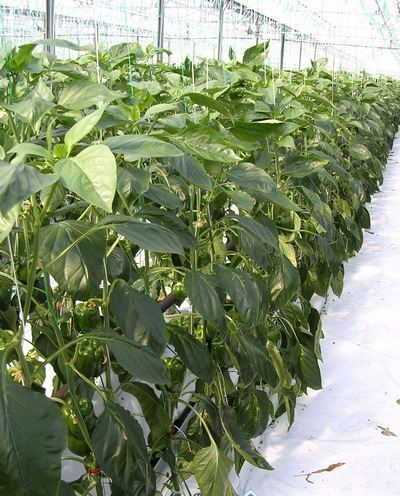 |
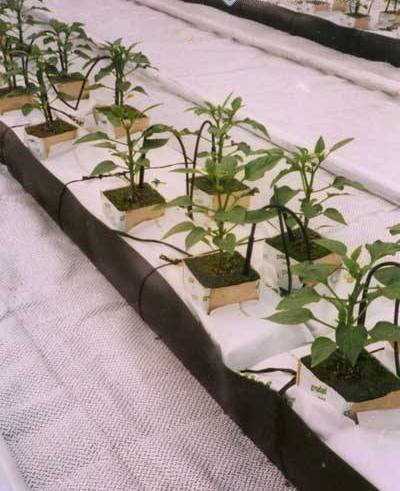 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| |
|